Electric Hoists: Efficient Lifting Solutions in Modern Industry
In modern industrial production, construction, logistics, and warehousing, efficient, safe, and reliable lifting equipment is crucial for smooth operational processes. As a widely used electric lifting tool, electric hoists have become indispensable in numerous industries due to their unique structural advantages and operational features. This article will comprehensively analyze the electric hoist's operating principle, structural features, application scenarios, technical advantages, and maintenance, exploring its value in detail.
I. Core Operating Principle and Structural Components
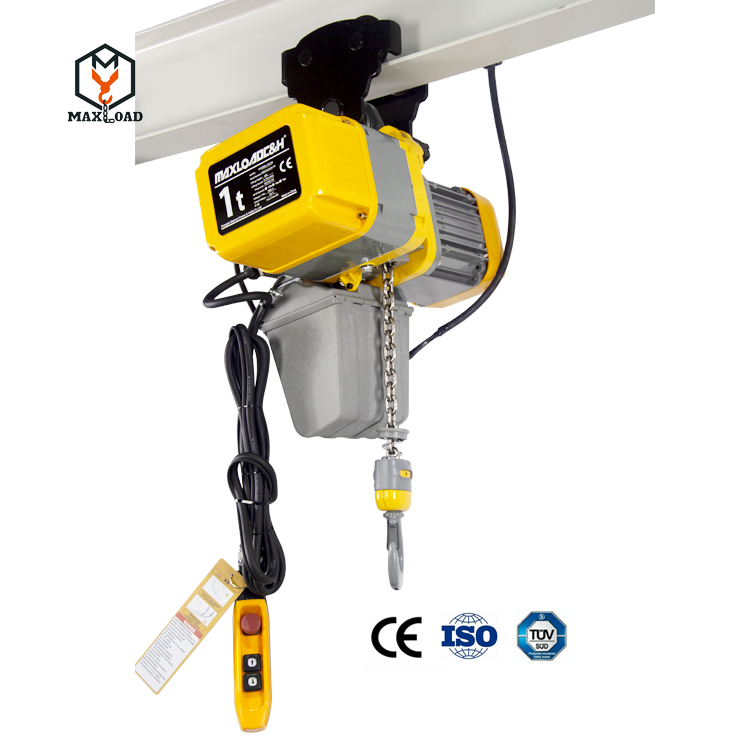
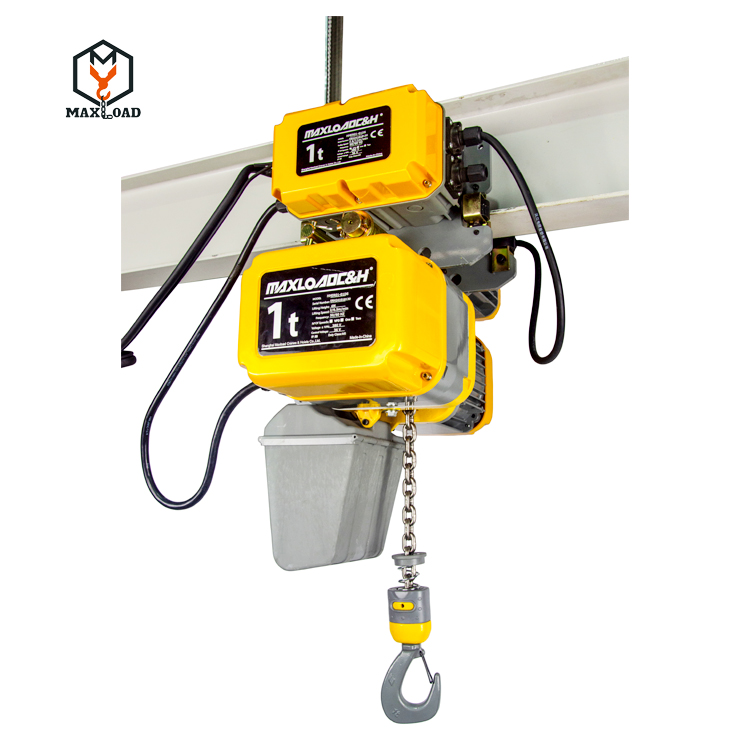
The core function of an electric hoist is to move loads vertically or horizontally through an electric drive. Its basic operating principle is based on the synergy between a motor drive and a mechanical transmission system. When the motor is activated, electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy, which is reduced in speed and increased in torque by a speed reducer, driving the drum or sprocket to rotate. This movement of the wire rope wound around the drum or the chain engaged with the sprocket causes the hook to be raised or lowered. Some models also feature a travel mechanism that allows for lateral movement on tracks, extending the operating range. Structurally, an electric hoist consists of five main components: a drive motor, a reduction gear, a hoisting mechanism, a control system, and safety devices. The drive motor is typically a three-phase asynchronous motor or a DC motor, offering high torque, low noise, and long life. The reduction gear often utilizes a worm gear or planetary gear structure for efficient transmission. Depending on the model, the hoisting mechanism is divided into two types: a wire rope drum and a chain drum. The former is suitable for large-tonnage, long-distance operations, while the latter is more popular for small and medium-sized applications due to its compact size and ease of maintenance. The control system integrates pushbutton switches, a remote control, or an intelligent control module, supporting single-speed, dual-speed, and even variable-frequency speed regulation to meet diverse operational needs. Safety devices include limit switches, overload protection, and an emergency stop button, ensuring safe and reliable operation.

II. Diverse Types and Applications
Electric hoists can be categorized into several types based on their usage environment and functional requirements. Chain electric hoists, with their compact structure, light weight, and low cost, excel in limited spaces, such as workshops and warehouse shelves. Its chain drive reduces the risk of wire rope tangles and offers relatively low maintenance costs. Wire rope electric hoists, with their greater load capacity and higher operating heights, are commonly used in large factories, ports, terminals, and construction sites where heavy loads must be handled. Mini electric hoists, designed for lightweight applications in homes, small studios, or laboratories, are compact and easy to operate, making them suitable for lifting small equipment or materials.
Electric hoists have a wide range of applications. In industrial production, they are often used for material handling, equipment installation, and maintenance on production lines. In construction, they assist in lifting rebar, precast concrete components, and building materials. In warehousing and logistics, they are essential tools for loading and unloading goods, stacking, and palletizing. They are even used in specialized applications such as firefighting and stage construction.
III. Technical Advantages and Industry Value
Electric hoists offer significant technical advantages over traditional manual hoists or hydraulic lifting equipment. First, efficiency is improved. Electric drive significantly reduces labor costs and increases operation speed, especially in high-frequency, long-distance lifting tasks. Second, ease of operation: whether controlled by buttons or a remote control, it lowers the barrier to entry and reduces the risk of misoperation. Third, safety features are superior, with multiple safety devices effectively preventing accidents such as overloads, collisions, and falls, ensuring the safety of both personnel and equipment. Furthermore, electric hoists are relatively easy to maintain; regular lubrication and inspection of key components can extend their service life and reduce the total cost of ownership.From an industry perspective, electric hoists not only improve production efficiency but also promote the standardization and intelligentization of operating methods. For example, in the context of smart manufacturing, some high-end models have integrated sensors and IoT modules to enable remote monitoring, fault warnings, and data statistics, providing decision support for production management. Regarding environmental protection and energy conservation, the application of new motors and energy-saving control technologies has enabled electric hoists to excel in energy consumption control, aligning with the development trend of green manufacturing.
IV. Maintenance and Safety Tips
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the long-term and stable operation of electric hoists. Daily inspections should include checking for wear on the wire rope/chain, the temperature and noise levels of the motor and reducer, and the sensitivity of the limit switches and emergency stop buttons. Regular lubrication is key to reducing friction and extending the life of the equipment. A lubrication schedule should be developed based on the frequency of use and environmental conditions. Regarding safe use, operators should receive professional training and be familiar with the equipment's performance and operating procedures. Overloading or illegal operation is strictly prohibited. Regular safety inspections should also be conducted to ensure the proper functioning of all safety devices to avoid accidents caused by equipment aging or malfunction.

V. Development Trends and Future Outlook
Electric hoists are developing towards intelligent, modular, and green features. Intelligence is reflected in the integration of more sensors and control modules to enable automatic positioning, path planning, and remote monitoring. Modular design facilitates rapid configuration for different scenarios, increasing flexibility. Green features reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions through the use of high-efficiency motors, energy-saving control systems, and environmentally friendly materials. Furthermore, the use of lightweight and high-strength materials makes the equipment more portable while maintaining strength, making it suitable for a wider range of specialized scenarios.
As an indispensable lifting device in modern industry, electric hoists play a vital role in numerous industries thanks to their efficiency, safety, and flexibility. With the continuous advancement of technology, electric hoists will continue to develop towards intelligent and green development, providing stronger support for improving production efficiency and ensuring safety across various industries. Understanding their operating principles, selecting the right type, and implementing standardized operation and scientific maintenance are key to fully realizing their value.


 0086 17717607077
0086 17717607077
 0086 (021) 5999 9072
0086 (021) 5999 9072
 market@chnhoist.com
market@chnhoist.com