Precise Collaboration: The Art of Industrial Symbiosis
In modern production workshops, bustling port terminals, or large equipment installation sites, one often sees this scene: a cleverly designed cantilever crane stands beside a workstation, its flexible boom supporting a stable and precise electric hoist that lifts and moves heavy objects. This seemingly simple combination of movement and stillness constitutes a highly efficient and reliable "golden partnership" in industrial material handling, playing an irreplaceable role in improving operational efficiency and ensuring production safety.
I. Material Handling Experts Each Performing Their Duties
To understand why this combination is so efficient, it is necessary first to analyze its core functions and characteristics.
JIB Crane: The Flexible Positioning "Mechanical Arm"
JIB cranes, often called jib cranes or cantilever cranes, are a relatively simple type of rotary crane. Its core components include:
Column: Serving as the main support for the entire equipment, it is usually fixed to the ground or suspended from a wall or roof structure, providing a stable foundation.
Cantilever: A horizontal or slightly inclined boom that extends the lifting operation. It can be designed with a fixed length or with telescopic functionality; some models also allow the cantilever to tilt within a certain angle range to adjust the working radius.
Slewing Mechanism: The core component driving the cantilever to rotate horizontally around the column. Rotation can be manual or motor-driven, achieving comprehensive coverage.
End Unit: The free end of the cantilever, used to suspend the lifting actuator, such as an electric hoist.
The core advantage of JIB cranes lies in their excellent positioning flexibility and space economy. Without a complex track system, it can quickly and accurately deliver loads to designated points within a fan-shaped or circular area centered on its column and with the cantilever length as its radius. This design is particularly suitable for frequent lifting operations at fixed workstations, such as loading and unloading machine tools, transporting components on assembly lines, and retrieving tools and parts from maintenance areas, effectively replacing manual handling and reducing worker fatigue and risks.
Electric Hoist: The "Power Hand" for Efficient Lifting
An electric hoist is a compact lifting device integrating a motor, reduction mechanism, drum (or sprocket), hook, and control system. Electric hoists are mainly classified into two categories based on the lifting medium: wire rope electric hoists and chain electric hoists. Their core function is to provide stable and controllable vertical lifting power.
A typical electric hoist usually includes:
Drive and transmission system: The motor provides power, which, through a precision gear reduction mechanism, converts high-speed rotation into low-speed, high-torque output, driving the drum to wind up and unwind the wire rope or the sprocket to drive the chain.
Bearing mechanism: The wire rope or lifting chain is responsible for directly bearing and transmitting the load.
Lifting device: Standard hooks, special lifting tools, or electromagnetic chucks, etc., are used to connect the load.
Control system: Usually operated via a hanging button station or remote control, realizing the control of lifting, and possibly lateral movement.
Safety devices: Overload protection, upper and lower limit switches, emergency power-off, etc., are crucial to ensuring safe operation.
The core value of electric hoists lies in their powerful lifting capacity, smooth speed control, high repeatability, and ease of integration. They can safely and effortlessly lift heavy objects from the ground or lower positions to the required height.
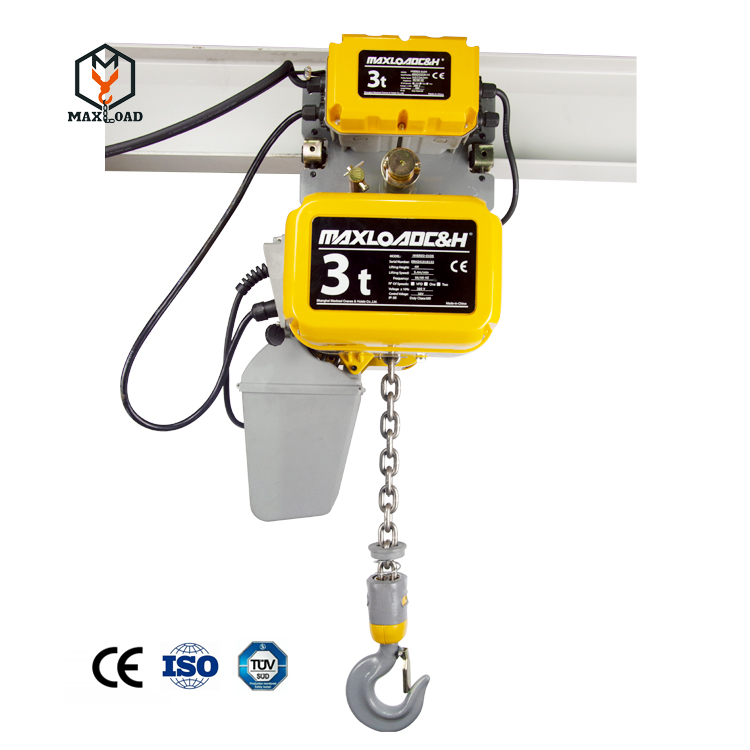

II. 1+1>2 Efficiency Integration
When the electric hoist is used as a lifting and retrieval device, suspended at the end of the JIB crane's boom, the two achieve perfect functional complementarity and integration, generating a significant synergistic effect:
Precise Handling with Full Three-Dimensional Coverage: The JIB crane solves the horizontal positioning problem, while the electric hoist precisely handles vertical lifting and lowering. Operators can easily lift heavy objects to any point in three-dimensional space by simply rotating the boom and operating the hoist buttons, achieving near-robotic arm flexibility, but with lower cost and application barriers.
Significantly Improved Work Efficiency and Reduced Labor Intensity: In fixed workstations or limited areas, this combination eliminates the need for large overhead cranes, allowing for on-demand access and significantly reducing mate.It completely liberates workers from heavy and dangerous manual handling, enabling the easy movement of objects weighing hundreds of kilograms to several tons.
Superior Space Adaptability and Economy: JIB cranes have a compact structure, occupying little or no floor space, making them particularly suitable for installation in space-constrained workshops, next to production lines, warehouse corners, or equipment maintenance areas. Compared to complete bridge crane systems, their installation costs and requirements for factory structures are lower, making them the economical choice for achieving partial automated material handling.
Enhanced Safety and Operability: The mechanized and controlled lifting process significantly reduces the risk of workplace injuries, such as crushing and twisting injuries caused by manual handling. The smooth starting and braking performance of the electric hoist avoids violent load swaying. Operators typically operate close to the load on the ground, with good visibility and direct control, improving operational safety.
III. Ubiquitous Industrial Assistant
The combination of electric hoists and JIB cranes, due to their flexibility and efficiency, has penetrated numerous industrial sectors: Machining and Assembly Workshops,Loading and unloading CNC machine tools and machining centers; transporting molds and workpieces; conveying large components such as engines and gearboxes on assembly lines.
Equipment Repair and Maintenance Area: Located next to the repair pit and in the equipment inspection area, used for hoisting disassembled motors, pumps, gearboxes, etc., facilitating maintenance work.
Warehouse and Logistics Center: Located on the loading and unloading platforms and racking areas of the warehouse, used for handling bundled goods, pallets, or heavy materials.
Automotive Manufacturing and Repair: Used for handling automotive body panel molds and engine assemblies.
Laboratory and Testing Center: Used for safely and smoothly hoisting precision instruments, testing equipment, or heavy samples.
New Energy Field: Used for material handling in battery pack production lines, photovoltaic panel installation, etc.
IV. Key to Achieving Optimal Matching
Selecting the appropriate combination of electric hoists and JIB cranes for specific application scenarios requires comprehensive consideration of the following factors:
Load Requirements: Determine the maximum lifting capacity, as well as the common shape, size, and hoisting method of the load.
Working Range: Determine the required coverage radius and lifting height. The rotation angle of the JIB crane also needs to be selected based on the site obstacles.
Usage Frequency and Working Level: Is it used frequently every day or only occasionally? This determines the working level of the equipment and affects the selection of motors and structural components.
Installation Environment and Conditions: Assess the load-bearing capacity, space dimensions, power supply conditions, and environmental factors of the installation location to select an appropriate protection level and structural form.
Safety and Control Requirements: Based on the operating conditions, confirm whether safety features such as dual-speed control, precise positioning, anti-sway function, overload protection, limit switches, and emergency stop are required. The operation method also needs to be considered.

Compliance: Ensure that the selected equipment complies with local or industry safety regulations and standards, and that installation and periodic inspections are performed by qualified professionals.
Conclusion: The combination of electric hoists and JIB cranes is not simply a matter of adding equipment together, but a proven, highly integrated material handling solution. It integrates fixed-point vertical lifting with flexible horizontal movement, providing an efficient, economical, and safe solution to the "last mile" material handling challenge in modern industrial production with its modular and compact design. In today's era of deepening smart manufacturing and lean production concepts, this classic equipment combination will continue to play a fundamental role in improving operational efficiency, ensuring personnel safety, and optimizing space utilization, becoming an indispensable "mechanical arm" for modern factories, thanks to its reliable performance and continuous evolution. Real waiting and handling time.


 0086 156 1824 5535
0086 156 1824 5535
 0086 156 1824 5535
0086 156 1824 5535
 kimliu@chnhoist.com
kimliu@chnhoist.com